GLIOBLASTOMA TREATMENT - GLIOVAC/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP EARLY ACCESS PROGRAM
Early Access to GLIOVAC/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP
Despite best efforts, it is not possible for all patients to participate in clinical trials. For that reason, ERC has established an early access program in a number of regions.
In the U.S., Right-to-Try (RTT) can be used to make promising products available to patients facing serious or life-threatening conditions. An eligible physician may request access to one of ERC’s investigational products by completing the ERC Right to Try Request Form. For more information please contact Benjamin Freilich MD benfmd@erc-usa.com
In Australia, Category A of the TGA Special Access Scheme (SAS) can be used to make promising products available to patients facing serious or life-threatening conditions. An eligible physician may request access to one of ERC’s investigational products by completing the ERC Special Access Scheme Request Form.
Requests for further information about how to apply for RTT or SAS or determine qualifications and capabilities required to administer ERC investigational product can be made to medicalaffairs@erc-immunotherapy.com
ERC is also willing to consider early access requests outside of these regions.
ERC typically will acknowledge receipt of a request, with required medical documentation, within three business days. ERC professionals will carefully consider requests taking into account access to open and accruing clinical trials, the serious/life-threatening nature of the disease, biological rational or clinical data supporting potential benefit medical appropriateness, and applicable laws and regulatory requirements. All physicians who receive ERC investigational product through RTT or SAS are required to comply with all applicable laws and regulations, and contractual conditions, including those related to safety reporting.
ERC’s Right to Try Policy can be found here.
ERC’s Special Access Scheme Policy can be found here.
Read more
The scientific staff
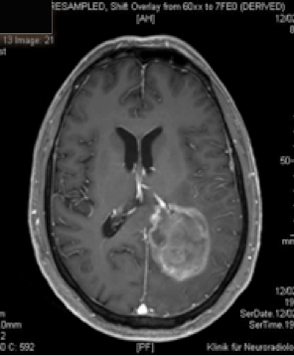
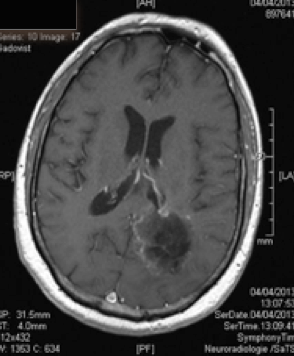
Action mechanism of Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP
Indeed, tumour cells express specific surface antigens. These antigens are not produced by healthy cells but are specific to tumour cells and are common between patients with the same tumour type.
By using non-proliferative cancer cell transplantation, it is not just one cancer-related antigen, but a whole set of tumour antigens associated to the glioblastoma, that is inoculated.
By using three different donors, the set of TAA is even broader. Injection of the autologous vaccine preparation will amplify the response of immune cells targeting the TAA present in the patient that is treated.
Upon activation, effector lymphocytes of the immune system are able to identify non-self tumour antigens and destroy the cancer cells that carry these antigens. The immune cells will proliferate and ensure the surveillance within the body, the cancer cells detection, their destruction and eventually patient recovery and immune resistance against the tumor.
Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP is an advanced immunotherapy based on transplantation of tumour cells and lysates in order to stimulate immunity to reject cancer cells [endif]--(Stathopoulos et al. 2008; Stathopoulos A 2012b, 2012a, Bota et al., 2015; Schijns et al., 2015). Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP is a cancer treatment composed of a combination treatment consisting of autologous glioma tumor cells, and allogeneic glioma tumour cells, generated from three different glioma donor cancer patients, and the lysates of all of these cells. Upon intradermal administration of glioma cancer treatment Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP, the mixture of the autologous and allogeneic vaccine (cells and lysates) stimulates the immune system to mount an immune response against glioma tumour-associated antigens, which leads to the destruction of glioma tumour cells.
By using non-proliferative cancer cell transplantation, it is not just one cancer-related antigen, but a whole set of tumour antigens associated to the glioblastoma, that is inoculated.
By using three different donors, the set of TAA is even broader. Injection of the autologous vaccine preparation will amplify the response of immune cells targeting the TAA present in the patient that is treated.
Upon activation, effector lymphocytes of the immune system are able to identify non-self tumour antigens and destroy the cancer cells that carry these antigens. The immune cells will proliferate and ensure the surveillance within the body, the cancer cells detection, their destruction and eventually patient recovery and immune resistance against the tumor.
Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP is an advanced immunotherapy based on transplantation of tumour cells and lysates in order to stimulate immunity to reject cancer cells [endif]--(Stathopoulos et al. 2008; Stathopoulos A 2012b, 2012a, Bota et al., 2015; Schijns et al., 2015). Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP is a cancer treatment composed of a combination treatment consisting of autologous glioma tumor cells, and allogeneic glioma tumour cells, generated from three different glioma donor cancer patients, and the lysates of all of these cells. Upon intradermal administration of glioma cancer treatment Gliovac/ERC1671/SITOIGANAP, the mixture of the autologous and allogeneic vaccine (cells and lysates) stimulates the immune system to mount an immune response against glioma tumour-associated antigens, which leads to the destruction of glioma tumour cells.
Read more